

- #MICROSOFT EXCHANGE SERVER FOR OUTLOOK 2013 SOFTWARE#
- #MICROSOFT EXCHANGE SERVER FOR OUTLOOK 2013 WINDOWS#
This void has however been filled by ISVs and storage manufacturers, through "site resilience" solutions, such as geo-clustering and asynchronous data replication. In this scenario, the data can be regarded as a single point of failure, despite Microsoft's description of this set-up as a "Shared Nothing" model. The clustering in Exchange Server provides redundancy for Exchange Server as an application, but not for Exchange data.

In fact, support for active-active mode clustering has been discontinued with Exchange Server 2007.Įxchange's clustering (active-active or active-passive mode) has been criticized because of its requirement for servers in the cluster nodes to share the same data. Subsequent performance issues with active-active mode have led Microsoft to recommend that it should no longer be used. They must wait, inactive, for the home servers in the node to fail. This is opposed to Exchange's more common active-passive mode in which the failover servers in any cluster node cannot be used at all while their corresponding home servers are active. In this setup, both servers in the cluster are allowed to be active simultaneously. Exchange Server 2003 also introduced active-active clustering, but for two-node clusters only.
#MICROSOFT EXCHANGE SERVER FOR OUTLOOK 2013 WINDOWS#
#MICROSOFT EXCHANGE SERVER FOR OUTLOOK 2013 SOFTWARE#
The standard SMTP protocol is used to communicate to other Internet mail servers.Įxchange Server is licensed both as on-premises software and software as a service (SaaS). This was discontinued in favor of Microsoft Outlook.Įxchange Server primarily uses a proprietary protocol called MAPI to talk to email clients, but subsequently added support for POP3, IMAP, and EAS.
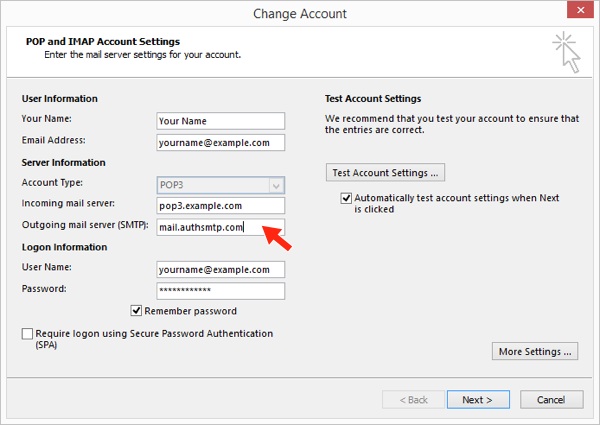
Until version 5.0 it came bundled with an email client called Microsoft Exchange Client. Exchange initially used the X.400 directory service but switched to Active Directory later. The first version was called Exchange Server 4.0, to position it as the successor to the related Microsoft Mail 3.5. It runs exclusively on Windows Server operating systems. Microsoft Exchange Server is a mail server and calendaring server developed by Microsoft.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
